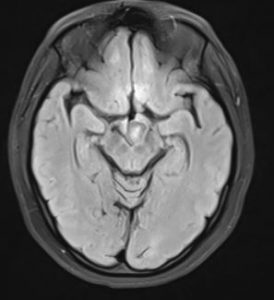
FINAL DIAGNOSIS : Hypothalamic Hamartoma
They were said to have signal intensity similar to normal cortex on all sequences, this is in fact not true in most cases 7.
- T1
- hypointense to the cerebral cortex (74%) 7
- T1 C+ (Gd): no contrast enhancement
- T2
- hyperintense to the cerebral cortex (93%) 7
- hyperintensity is more conspicuous on FLAIR
- the higher the proportion of glial cells, the higher the T2 signal 3
- MR spectroscopy
- reduced NAA/Cr
- increased myoinositol 3
- increased Cho/Cr compared to the amygdala has also been reported
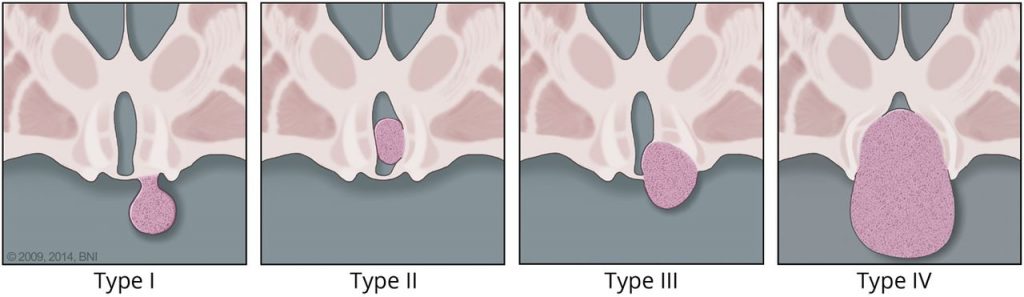
Delalande Classification of Hypothalamic Hamartomas
- Type I lesions have horizontal attachment inferior to floor of the third ventricle.
- Type II lesions have vertical attachment to the wall of third ventricle and are above the floor of the third ventricle.
- Type III lesions have horizontal and vertical attachments above and below the floor of the third ventricle.
- Type IV lesions are considered “giant” with volume 8 cm3 or larger
The differential diagnosis is broadly that of suprasellar/hypothalamic lesions, although the imaging characteristics of hypothalamic hamartomas significantly reduce the differential.
Hypothalamic-chiasmatic glioma is the main differential. Most other lesions encountered in the region either have markedly different signal intensity or demonstrate enhancement.